Product traceability consists of following a part and its components throughout its entire life cycle.
This requires the implementation of a system capable of gathering and managing information relating to the different stages of production and distribution.
But why is it so important to track products throughout their lifespan? What are the objectives sought through this approach?
Here are the main challenges of industrial traceability.

Why is product traceability important?
Data traceability is a key process for optimizing production in an industrial environment and ensuring precise internal and external quality monitoring throughout the product lifespan.
In particular, it allows you to obtain valuable data such as:
- a history of the origin of the pieces;
- information on product assembly;
- control points on the quality of parts;
- verification elements in the event of a malfunction.
| Example of traceability in the automotive industry | |
|
|
In many industries, particularly in the automotive sector, this part marking for traceability purposes is generally linked to standards and regulations. It can be applied to all or some of the parts, from the front bumper to the exhaust system. It is useful for their entire lifespan, especially when it comes to parts with a potential impact on human safety, and even at the very end, when recycling is required. When the parts are identified, it is possible to easily replace them, carry out a mass recall on vehicles with a defective part, or facilitate their repair. Finally, the traceability process also makes it possible to identify certain materials to be recovered or certain pollutants to be treated. |
|
Do you want to discuss a part marking project? |
In a context of globalization which remains the norm today, industrial companies need to remain competitive, and therefore to constantly improve their production processes with appropriate tools. Which calls for manufacturers to be able to:
- ensure just-in-time production ;
- lower the costs manufacturing their products;
- optimize their production process ;
- gain flexibility with their suppliers and partners.
So many constraints that force companies to organize themselves to monitor their production and ensure its pace.
As a result, industrial traceability and product marking makes it possible to ensure a certain fluidity in the production process, and to act effectively in the event of a problem with a product. But concretely, what are its different objectives?
Industrial traceability: definition, objectives and benefits
Thanks to a unique serial number encoded in barcode or a 2D code, products marked at the end of production can be identified and tracked after they leave the plant. Part marking allows, depending on the needs:
- to ensure quality monitoring of the product throughout its lifespan;
- to identify the parts with design or production defects;
- to initiate corrective measures, which can go as far as recalling the incriminated parts.
The serial number must then be recorded in the customer's information system, with the batch reference and its manufacturing date. The goal: to be able to recall all of the parts concerned if necessary and protect the end consumer.

Part marking and tracking solutions make it possible to carry out automatic checks during production.
Being able to identify parts during a manufacturing process serves, in particular, to check that the components presented correspond to the process in the event of assembly. Automatic control which makes it possible to limit human errors, and therefore reduction in production.

By tracking your products, you can also implement a total quality system. In this case, it involves product marking all the parts from the first stage of production, and re-reading the marking at each operation until the end of the manufacturing process.
The part can then be associated with each machine on which it has passed.
-
This allows you to know exactly which batches of parts are defective in the event of a problem. Through this, you can request the return of only the parts produced on a given machine, without needing to recall all the products manufactured and sent to consumers during the period concerned.
-
You can also optimize production processes, thanks to the information provided on scrap eliminated during production, which can allow you to trace it back to the responsible machine. This preventive action is much more effective than a costly recall.

The stages of industrial traceability
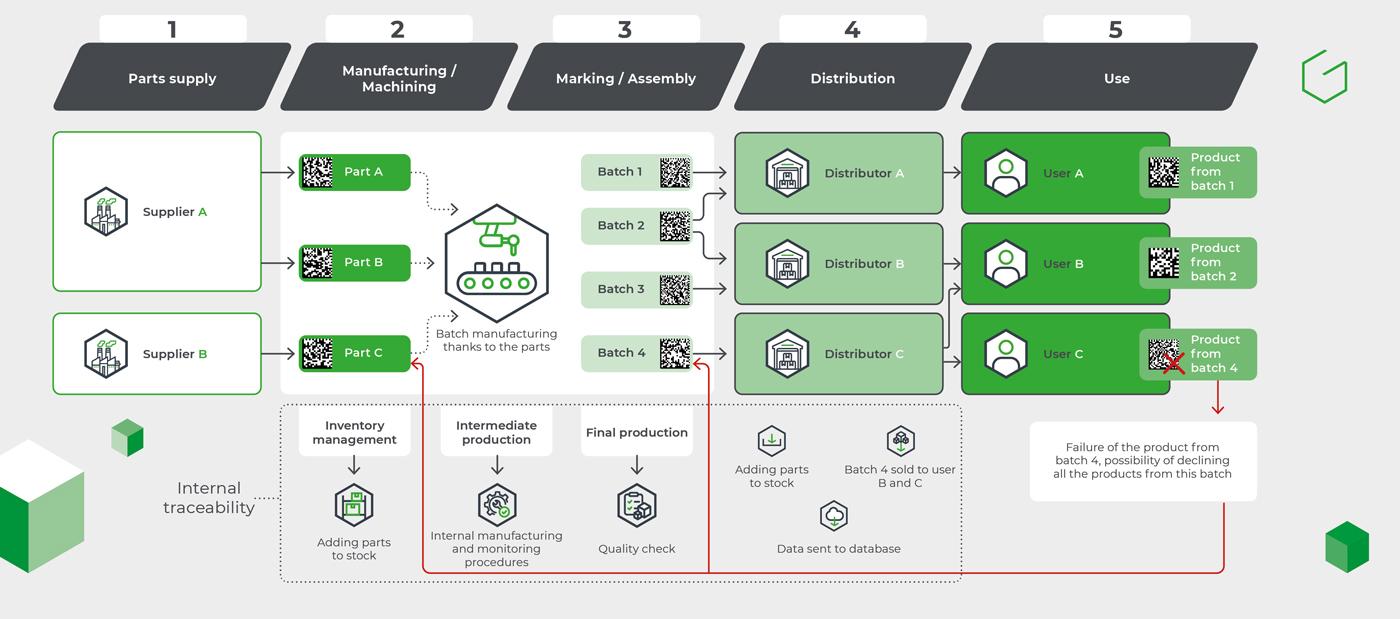
- Parts sourcing and supply
Several suppliers send their parts and raw materials, without them necessarily having an identification code.
- Manufacturing/Machining
Upon receipt of the parts, an identification code is assigned and this is returned to stock to be followed throughout the transformation of the product
- Marking/Assembly
Batches of transformed parts have a new number to identify which ones are part of the lot.
- Distribution
The distribution network enters the part into stock according to the identification code provided and then assigns a user.
- Use
The identification code will allow, going up the chain, to reach the distributor thanks to the batch number as well as the part and supplier references.
In the product marking and traceability process, the ability of the marking machine to communicate well and integrate into the data flow is essential. It must be able to communicate with the ERP software, the line controller and other machines to receive and report data.
Do you want to discuss a product marking project?